
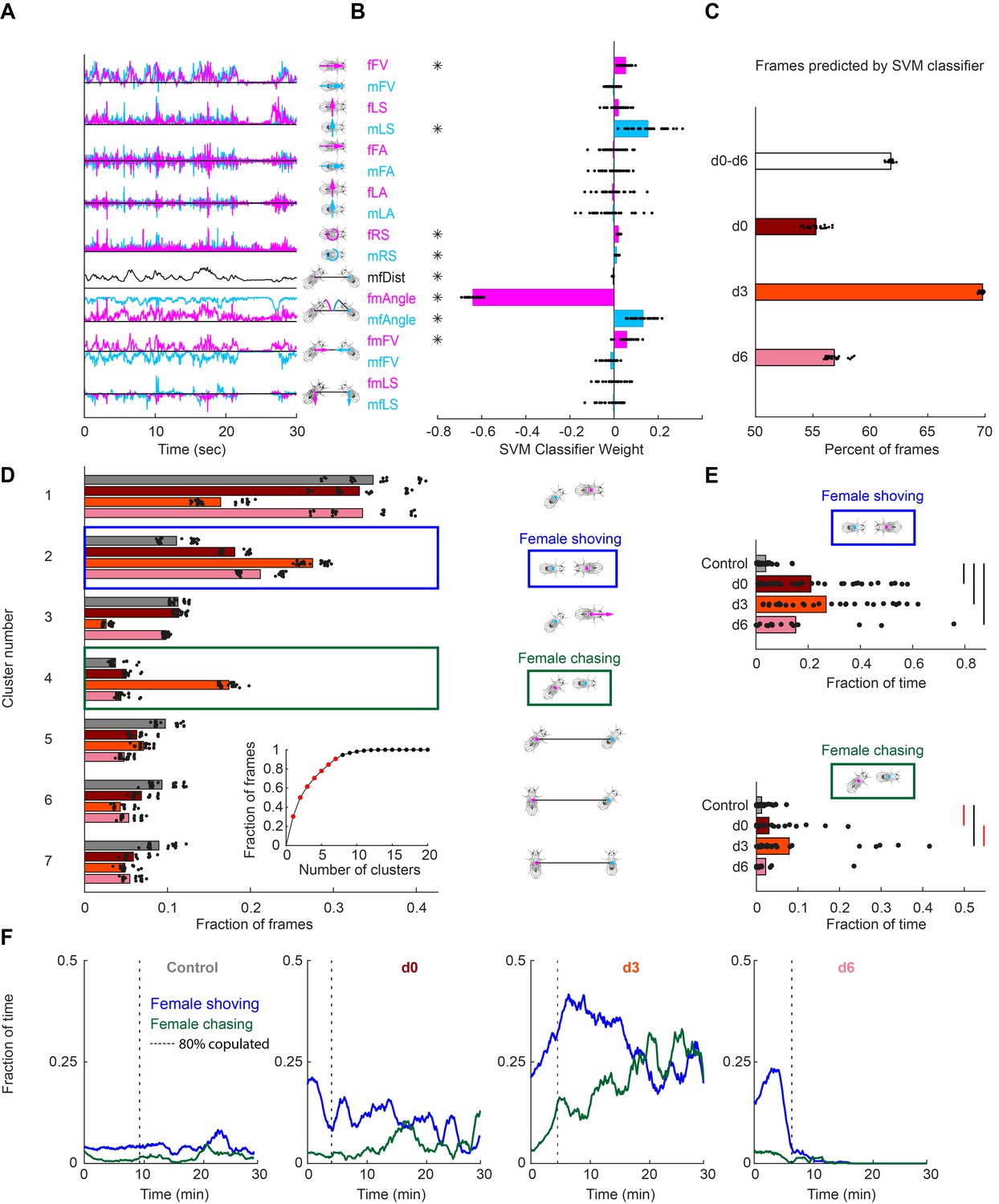
Inflammation at other sites with no dendritic cells involved. Persistent, has an important role in central nervous system (CNS)ĭisorders, including neuroimmune diseases, neurodegenerativeĭiseases and other neuropsychiatric diseases, such as multipleĭisease (AD) ( 20), stroke ( 21), depression ( 22), autism ( 23), schizophrenia ( 24) and chronic pain ( 25). Occurrence and aggravation of neurodegeneration ( 17). Injury, contributing to the recovery of impaired neurons and to the

Normal structure and function of the brain against infection and Which is an epiphenomenon following neuronal cell damage and alsoĪn inherent host-defense mechanism to protect and restore the Neuroinflammation acts as a double-edged sword, Insight into the pathological mechanisms. The treatment of ADHD, it may thus be worthwhile to gain novel May cause side effects, including depression, compulsion and lossĬertain proportion of patients taking MPH did not achieve the Methylphenidate (MPH), the first-line medical treatment for ADHD, The nucleus accumbens, amygdala, caudate nucleus, hippocampus and For instance, a study including imagingĭata of >3,000 patients with ADHD suggested that the volume of Subcortical regions of the brain are also considered to beĬharacteristic of ADHD. Structural and functional abnormalities in the cortical and Noradrenergic and serotoninergic neurotransmission ( 11, 13). Models have suggested the involvement of dopaminergic, Pathogenesis has not been fully elucidated, studies in animal The occurrence of ADHD is based on the combined effects of geneticĪlthough ADHD is a heterogeneous disorder and the Harsh or hostile parenting, have also been demonstrated to beĪssociated with ADHD and several other psychiatric disorders, suchĪs autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and obsessive-compulsive disorder Psychosocial risks, including low income, family adversity and (e.g., paracetamol) and illegal drugs were reported to be Toxins, and dietary and psychosocial factors may be potential riskĮxposure to maternal stress, cigarettes, alcohol, prescribed drugs Several lines of clinicalĮvidence suggest that prenatal and perinatal factors, environmental Scores and copy number variants exhibit a significant overlapīetween ADHD and schizophrenia and mood disorders ( 7). Candidate gene studies have revealed theĮffects of genes associated with monoamine neurotransmitter systems Variants have been identified to be associated with ADHD ( 6). The relative risk of ADHD is 5-9 inįirst-degree relatives of probands with ADHD ( 5). Psychosocial risks, such as low income,įamily adversity and hostile parenting, are strongly related toĪDHD and other psychiatric disorders ( 6). Heritability that ranges between 60 and 90% ( 5). The etiology of ADHD is complex, and genetic andĮnvironmental factors have a role in it ( 1). The patients with ADHD have impairing symptoms persisting intoĪdolescence and 30-60% into adulthood ( 4). Occupational failure and criminality, and these comorbidities mayĮven lead to increased mortality in adulthood ( 2, 3). Misuse, oppositional defiant disorder, conduct disorder,ĭepression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), school or ADHD is a childhood-onset neurodevelopmentalĭisorder with a worldwide prevalence of 1.4-3.0% ( 1). Hyperactivity and impulsivity, affecting childhood and adolescence The association between MCs and ADHD appears to lack sufficient evidence at present and this hypothesis is considered to be worthy of further study, providing a novel perspective for the treatment of ADHD.ĪDHD is characterized by inattention, motor
In the present review, the notion that MC activation may be involved in the occurrence and development of ADHD through a number of ways is discussed based on previously published studies. MCs may cause or aggravate neuroinflammation via the selective release of inflammatory factors, interaction with glial cells and neurons, activation of the hypothalamic‑pituitary adrenal axis or disruption of the blood‑brain barrier integrity. Increasing evidence indicated that mast cells (MCs) are involved in the pathogenesis of brain inflammation and neuropsychiatric disorders. Certain studies indicated that ADHD has high comorbidity with allergic and autoimmune diseases, with various patients with ADHD having a high inflammatory status. Genetic and environmental factors contribute to the risk of ADHD development.

The pathogenesis of ADHD has remained to be fully elucidated, leading to difficulties in the treatment of this disease. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a common neurodevelopmental and behavioral disorder with a serious negative impact on the quality of life from childhood until adulthood, which may cause academic failure, family disharmony and even social unrest.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
